त्रिक गुणनफल
नेविगेशन पर जाएँ
खोज पर जाएँ
सदिश बीजगणित में तीन ३-विमीय सदिशों का गुननफल त्रिक गुणनफल (triple product) कहलाता है। दो तरह के त्रिक गुणनफल होते हैं- अदिश मान वाला त्रिक गुणनफल तथा सदिश त्रिक गुणनफल।
अदिश त्रिक गुणनफल
- <math>{a}\cdot({b}\times{c}) = {c}\cdot({a}\times{b}) = {b}\cdot({c}\times{a})</math>
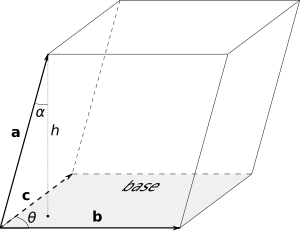
इस गुणन्फल का मान तीनों सदिशों <math>\mathbf{a}</math>, <math>\mathbf{b}</math> और <math>\mathbf{c}</math> से बने हुए समान्तरषटफलक के आयतन के बराबर होता है।
गुण
- चक्रीय शिफ्ट करने पर अदिश त्रिक गुणनफल (a, b, c) का मान नहीं बदलता। :
- <math>
\mathbf{a}\cdot(\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{c})=
\mathbf{b}\cdot(\mathbf{c}\times \mathbf{a}) =
\mathbf{c}\cdot(\mathbf{a}\times \mathbf{b})
</math>
- Swapping the positions of the operators without re-ordering the operands leaves the triple product unchanged. This follows from the preceding property and the commutative property of the dot product.
- <math>
\mathbf{a}\cdot (\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{c}) \equiv
(\mathbf{a}\times \mathbf{b})\cdot \mathbf{c}
</math>
- Swapping any two of the three operands negates the triple product. This follows from the circular-shift property and the anticommutativity of the cross product.
- <math>\begin{align}
&\mathbf{a}\cdot(\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{c}) \\
\equiv -&\mathbf{a}\cdot(\mathbf{c}\times \mathbf{b}) \\
\equiv -&\mathbf{b}\cdot(\mathbf{a}\times \mathbf{c}) \\
\equiv -&\mathbf{c}\cdot(\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{a})
\end{align}</math>
- The scalar triple product can also be understood as the determinant of the साँचा:gaps matrix (thus also its inverse) having the three vectors either as its rows or its columns (a matrix has the same determinant as its transpose):
- <math>\mathbf{a}\cdot(\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{c}) \equiv \det \begin{bmatrix}
a_1 & a_2 & a_3 \\ b_1 & b_2 & b_3 \\ c_1 & c_2 & c_3 \\
\end{bmatrix}={\rm det}\left(\mathbf{a},\mathbf{b},\mathbf{c}\right) .</math>
- If the scalar triple product is equal to zero, then the three vectors a, b, and c are coplanar, since the parallelepiped defined by them would be flat and have no volume.
- If any two vectors in the triple scalar product are equal, then its value is zero:
- <math>
\mathbf{a} \cdot (\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{b}) \equiv
\mathbf{a} \cdot (\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{a}) \equiv
\mathbf{a} \cdot (\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{b}) \equiv
\mathbf{a} \cdot (\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{a}) \equiv 0
</math>
- Moreover,
- <math>
[\mathbf{a}\cdot(\mathbf{b}\times \mathbf{c})] \mathbf{a} \equiv
(\mathbf{a}\times \mathbf{b})\times (\mathbf{a}\times \mathbf{c})
</math>
- The simple product of two triple products (or the square of a triple product), may be expanded in terms of dot products:[१]साँचा:paragraph breakसाँचा:glossaryसाँचा:defnसाँचा:glossary endसाँचा:paragraph breakThis restates in vector notation that the product of the determinants of two 3×3 matrices equals the determinant of their matrix product.
सदिश त्रिक गुणनफल
यह गुणनफल एक सदिश राशि होती है।
- a*(b*c)=(a.c)b-(a.b)c