अग्रोस२डी
नेविगेशन पर जाएँ
खोज पर जाएँ
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
इस लेख को हिन्दी में अनूदित करने की आवश्यकता है। यह लेख हिन्दी के अतिरिक्त अन्य भाषा में लिखा है। यदि यह लेख उस भाषा के समुदाय के लिए बनाया गया है, इसका योगदान उस भाषा के विकिपीडिया में किया जाना चाहिए। विकिपीडियाओं की सूची देखें। |
 | |
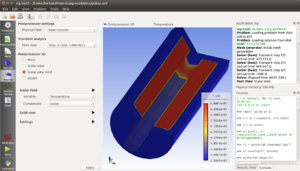 अग्रोस२डी द्वारा सिमुलेट किया गया ऊष्मा अन्तरण की एक समस्या | |
| Developer(s) | University of West Bohemia |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 3.2
/ March 3, 2014 |
| साँचा:template other | |
| Operating system | Linux, Windows |
| Available in | C++, Python |
| Type | Scientific simulation software |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | www |
अग्रोस२डी (Agros2D) एक मुक्तस्रोत है जो अनेक क्षेत्रों (जैसे स्थिरवैद्युतिकी, स्थिरचुम्बकत्व आदि) से सम्बन्धित द्विबीमीय समस्याओं (2D problems) का संख्यात्मक विश्लेषण करने में सहायक है। इसमें जीयूआई के माध्यम से समस्या का वर्णन तथा उसकी ज्यामिति, पदार्थ और सीमान्त मान का निर्धारण करने ( preprocessing) , समस्या का हल तथा हल के पश्चात उससे समन्धित आंकड़ों और तथ्यों का चित्रमय/ग्राफमय प्रस्तुतीकरण (postprocessing) की सुविधा है।
विशेषताएँ
- बहु-क्षेत्रीय समस्याएँ (Coupled Fields) - With coupled field feature you can blend two or more physical fields in one problem. Weak or hard coupling options are available.
- अरैखिक समस्याएँ (Nonlinear Problems) - Simulation and analysis of nonlinear problems are available. Agros2D now implements both Newton’s and Pickard’s methods.
- स्वतः स्पेस और समय का उपयुक्त चुनाव (Automatic space and time adaptivity) - One of the main strengths of the Hermes library is an automatic space adaptivity algorithm. With Agros2D is also possible use adaptive time stepping for transient phenomena analysis. It can significantly improve solution speed without decreasing accuracy.
- वक्र एलिमेन्ट्स - Curvilinear elements is an effective feature for meshing curved geometries and leads to faster and more accurate calculations.
- चतुर्भुजाकार मेशिंग (Quadrilateral Meshing) - Quadrilateral meshing can be very useful for some types of problem geometry such as compressible and incompressible flow.
- विद्युत/चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र में आवेशित कणों के पथ की गणना (Particle Tracing)—Powerful environment for computing the trajectory of charged particles in electromagnetic field, including the drag force or their reflection on the boundaries.
मुख्य क्षमताएँ
- Higher-order finite element method (hp-FEM) with h, p and hp adaptivity based on reference solution and local projections
- Time-adaptive capabilities for transient problems
- Multimesh assembling over component-specific meshes without projections or interpolations in multi-physics problems
- Parallelization on single machine using OpenMP
- Large range of linear algebra libraries (MUMPS, UMFPACK, PARALUTION, Trilinos)
- Support for scripting in Python (advanced IDE PythonLab)
विश्लेषण के भौतिक क्षेत्र
- स्थिरवैद्युतिकी (Electrostatics)
- Electric currents (steady state and harmonic)
- चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र (steady state, harmonic and transient)
- ऊष्मा अन्तरण (eat transfer) (steady state and transient)
- Structural mechanics and thermoelasticity
- Acoustics (harmonic and transient)
- Incompressible flow (steady state and transient)
- RF field (TE and TM waves)
- Richards equation (steady state and transient)
एक से अधिक क्षेत्र वाली समस्याएँ (Couplings)
- Current field as a source for heat transfer through Joule losses
- Magnetic field as a source for heat transfer through Joule losses
- Heat distribution as a source for thermoelastic field
इतिहास
The software started from work at the hp-FEM Group at University of West Bohemia in 2009. The first public version was released at the beginning of year 2010. Agros2D has been used in many publications.[१][२][३][४][५][६][७]
इन्हें भी देखें
सन्दर्भ
बाहरी कड़ियाँ
- ↑ Dolezel, I., Karban, P., Mach, F., & Ulrych, B. (2011, July). Advanced adaptive algorithms in finite element method of higher order of accuracy. In Nonlinear Dynamics and Synchronization (INDS) & 16th Int'l Symposium on Theoretical Electrical Engineering (ISTET), 2011 Joint 3rd Int'l Workshop on (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- ↑ Polcar, P. (2012, May). Magnetorheological brake design and experimental verification. In ELEKTRO, 2012 (pp. 448-451). IEEE.
- ↑ Lev, J., Mayer, P., Prosek, V., & Wohlmuthova, M. (2012). The Mathematical Model of Experimental Sensor for Detecting of Plant Material Distribution on the Conveyor. Main Thematic Areas, 97.
- ↑ Kotlan, V., Voracek, L., & Ulrych, B. (2013). Experimental calibration of numerical model of thermoelastic actuator. Computing, 95(1), 459-472.
- ↑ Vlach, F., & Jelínek, P. (2014). Determination of linear thermal transmittance for curved detail. Advanced Materials Research, 899, 112-115.
- ↑ Kyncl, J., Doubek, J., & Musálek, L. (2014). Modeling of Dielectric Heating within Lyophilization Process. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014.
- ↑ De, P. R., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Layek, G. C. (2012). Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer over a symmetric porous wedge. Acta Technica CSAV, 57(3), 227-237.